Baha® kemik iletimli implantlar
Dünyanın dört bir yanındaki kişiler, 35 yıldan uzun süredir seslere Baha® kemik iletimli implant ile ulaşıyor. Baha Sistemi, sesi kemik iletimi yoluyla ilerletmek için vücudun doğal yeteneğinden yararlanır ve işitme ve iletişim kurma seviyeniz üzerinde derhal ve olumlu bir etki yaratma potansiyeline sahiptir.
İşitmeye giden doğal yolunuz
Duyduğumuz birçok ses, kulağımıza havada yol alarak gelse de (hava iletimi), aslında çoğunu kemikteki titreşimler (kemik iletimi) sayesinde işitiriz. Normal işitme yeteneğine sahip bir kişi kendi ses tonunu işitirken, duyduklarının çoğu aslında kemik iletimi yoluyla gelir.
Dış ve orta kulağınızdaki sorunlar ses dalgalarının akışını bloke edebilir veya sınırlandırabilir ve bunların iç kulağınıza etkin bir şekilde ulaşmasına engel olabilir. Bir işitme cihazı, sesi sorunlu bu alanlardan geçirmek için yeterince zorlayabilme gücüne dayansa da, kemik iletimi implantları, sesi vücudun doğal şekilde iletme yeteneğinden yararlanır. Bu doğal süreçten tam anlamıyla yararlanmak, şimdiye dek hiç olmadığı kadar iyi ve net bir şekilde işitmenizi sağlayabilir.

Çalışma şekli
Bir işitme cihazı, sesi hasarlı alan üzerinden göndermeye çalışırken, Baha Sistemi sesi net, temiz şekilde doğrudan iç kulağınıza göndermek için kemik iletiminin avantajından yararlanır. Günümüzde iki tip Baha sistemi bulunmaktadır. Her ikisi de güvenle işitmenize ve iletişim kurmanıza yardımcı olmak üzere tasarlanmış eşsiz Cochlear teknolojisini sunar.
- Ses işlemcisi sesleri havada yakalar.
- Ses işlemcisi sesleri titreşimlere dönüştürür ve bunları abutment veya manyetik bağlantı üzerinden küçük implanta gönderir.
- İmplant, titreşimleri kemik yolu üzerinden iç kulağınıza doğrudan iletir.
Kemik iletimli sistemler nasıl çalışır (Ponto®)

Kemik iletimliı işitme sistemleri vücudunuzun kemik iletimi yoluyla ses aktarmak için doğal yeteneklerini kullanmak için tasarlanmıştır. Ses işlemcisi, sesleri titreşimlere dönüştürür ve titreşimler kafatası kemiğiyle doğrudan iç kulağınıza gönderilir.
Kemik iletimli bir işitme sistemi üç bölümden oluşur:
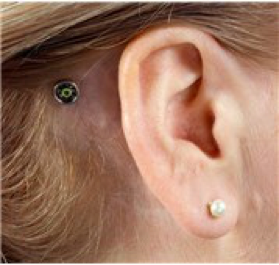
1. Kulağın arkasında kemiğe oturan küçük (3 veya 4 mm) titanyum implant
2. Ses işlemcisinin bağlanmasını sağlayan deriyle sorunsuz bir şekilde yerleştirilen bir abutment
3. Kulak arkasında duran ses işlemcisi
 |
 |
 |
Küçük titanium implant |
Konuşma işlemi takılmamış abudment |
Abudment üzerindeki konuşma işlemcisi |
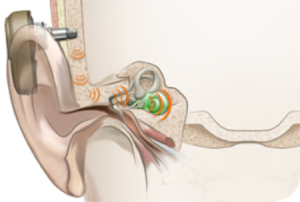
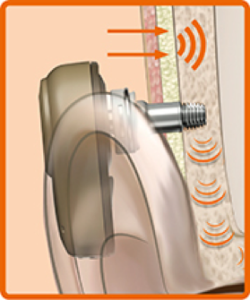
Kemik iletimi nasıl çalışır
Ses işlemcisi abutment üzerine kolaylıkla takılır. Bağlantı sağlandıktan sonra, ses dalgalarının toplanması, işitme cihazı gibidir. Bununla birlikte, bu ses dalgalarını dış kulak yolundan iletmek yerine, kafatası kemiklerinden iletmeye hazırlar ve ses dalgalarını titreşimlere dönüştürür. Ses işlemcisi ile implant ve abutment yoluyla kemik arasındaki doğrudan bağlantı sayesinde, cildiniz ses titreşimlerini hafifletmez ve daha net bir ses verir.
Ses işlemcisini çıkarırsanız, örneğin duş veya uyku gibi durumlarda, ses titreşimleri gönderilmez ve işitme cihazı orijinal durumuna dönecektir.
Ponto Sistemi Doğrudan Ses İletimine bir örnektir. Bu, cildin sistemlerine kıyasla en iyi amplifikasyonu ve çıktıyı sağlar; burada cilt, ses işlemcisi ve kemik arasında nem katman tabakası oluşturur.
Cerrahi teknik
Kemik iletimli işitme sistemi kazanılması, kanıtlanmış, güvenli ve nispeten basit bir işlemdir ve çoğunlukla lokal anestezi ile yapılır. Yeni Minimal İnvazif Ponto Cerrahisi ile implantın ve abutmentin boyutuna tam olarak uyacak şekilde küçük bir kesi yapılır. Bu dikiş ihtiyacını ortadan kaldırır, bu da cerrahide daha az zaman demektir. Bu işlemi yara izini de azaltır ve iyileşme süresini kısaltır.
Ayrıca, eğer kemiğe implante işitme sizin için doğru değilse karar verirseniz, cihaz çıkarılabilir.
Kemik iletimli işitme sisteminden kimler yararlanabilir?
İşitme kaybınız dış veya orta kulaklarınızdaki problemlerden kaynaklanıyorsa, odyoloğunuza, kemik bağlantılı cihazlar hakkında konuşun. Özellikle kulak kanalında veya orta kulaktaki tüm sorunları atlamak için tasarlanan bu cihazlar size daha net, daha rahat bir işitme sağlayabilir.
• Mikrotiya ve atrezisi gibi kulak kanalı ve orta kulak problemleri
• Tek taraflı total işitme kaybı
Med-El BoneBridge ®

Med-El BoneBridge, mikrotiya ve atrezisi olan hastalarda kullanılabilen, kemik iletimli işitsl implantların başka bir türüdür.
BoneBridge, dünyanın ilk aktif kemik iletimli implantıdır. Bu kemik iletimi, doğrudan kemik iletimiyle iç kulağa iletilmesini sağlar. BoneBridge, implantın tamamen cildin altına yerleştirildiği, yarı-implante edilebilir bir işitme sistemidir. İmplant, saçların altına takılan harici bir ses işlemcisinden sinyal alır.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Wfc3ymniURI
Med-El Vibrant Soundbridge®

Vibrant Soundbridge, mikrotia ve atrezisi olan hastalar için başka bir alternatif olan orta kulak implant sistemidir. Soundbridge, geleneksel işitme cihazlarına veya kemik iletim cihazlarına alternatiftir. Bu cihaz, harici olarak takılan ses işlemcisinden ve cerrahi olarak cildin altına yerleştirilen bir implanttan oluşur. Ses işlemcisi manyetik enerji ile tutulur ve saçların altına veya üstüne takılabilir. Sesler, ses işlemcideki mikrofon tarafından toplanır. Ses işlemcisi bu sesleri elektrik sinyallerine dönüştürür. Elektrik sinyalleri deriden implanta iletilir. İmplant, sinyali yüzer kütle transdüserine iletken bir bağlantı ile iletir. Orta kulaktaki inkus kemiğine t
akılan floating mass transducer, sinyalleri mekanik titreşimlere dönüştürür ve orta kulak yapılarını harekete geçirir. Orta kulak yapılarının hareketi titreşimi doğrudan iç kulak işitme organına gönderir.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ahrKaHrrmcw
İşitsel Beyin sapı İmplantı
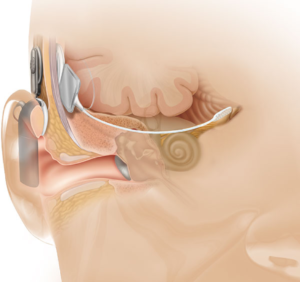
Bir işitsel beyin sapı implantının iki kısmı vardır: Dış Parça (‘işlemci’, kulak arkasına takılır) ve cerrahi olarak implante edilen iç parça. İşlemci üzerindeki bir mikrofon, etrafındaki sesi alır ve bir ses dalgasından elektriksel bir sinyal haline getirir. İşlemci ses sinyalini işitme implantının iç kısmına iletir. Bu, derinin hemen altındaki bir alıcının yanı sıra beyin sapı içine yerleştirilen implant diziliminden oluşur.
Bu, implantın hem kokleayı hem de işitme sinirini atllayarak, beyin sapına direkt ulaşır. İşitsel beyinsapı implantı, bu şekilde, işitme siniri ve iç kulak olamdığında veya çalışmadığında işitmeyi sağlamaya çalışan bir sistemdir.
Kimlere düşünülebilir?
İşitsel beyin sapı implantının temel kullanım alanlarından biri , Nörofibromatozis tip 2 (NF2) tümörü olanları hastalardır. NF2’ye sahipseniz, işitme sinirinin üzerinde veya yakınında bir tümör olması muhtemeldir. Tıbbi nedenlerden ötürü bu tümör çıkarılırsa, cerrahlar işitme sinirini kesmek zorunda kalabilirler. Bu, o kulaktaki doğal işitme hakkında tam bir kayıp. Tümör çıkarma operasyonu esnasında, cerrah alternatif bir işitme yöntemi olarak bir işitsel beyin sapı implant yerleştirmeyi düşünebilir.
İşitsel beyin sapı implantının diğer kullanımı, herhangi bir kulakta işitme siniri ya da iç kulak yapısının hiç olmamasıdır. Bazen menenjit de iç kulakda kireçlenme olur ve koklear implant takmak mümkün olmayabilir. Budurmda beyin sapı implantı takmak tek alterantif olarak kalır. Beyin cerrahisi işlemleri ile operasyon yapılır.
Olası Yararları nelerdir?
İşitsel beyin sapı implantı, doğal işitmesi olmayan kişilere işitme sistemi sağlayabilir. İşitsel bir beyinsapı implantı dudak okumaya yardımcı olabilir.
Komplikasyonları?
İşitsel bir beyin sapı implantı, kompleks bir beyin cerrahisi operasyonu ile takılabilir. Cerrahinizin sizinle olabilecek tüm riskleri tartışması gerekir.
İşitsel bir beyinsapı implantının sonuçları son derece değişkendir. İşitsel beyin sapı implantının beyin sapına tam olarak ses iletmek üzere yerleştirilmesi zor bir işlemdir. İşitsel beyin sapı implantından hiç işitme sağlanamaybilir.
Bazı durumlarda, işitme sınırlı olup, bu nedenle sesler iyi fark edilmez. İşitsel bir beyin sapı implantıyla algılanan sesin işlemlenmesi de zaman alır.
.
Cochlear Baha® Bone Conduction Implants
For more than 35 years, people all over the world have connected to sound through a Baha® bone conduction implant. The Baha System uses the body’s natural ability to conduct sound through bone conduction, and has the potential to make an immediate and positive impact on how well you hear and communicate.
Your natural pathway to hearing
While a lot of the sound we hear travels to our ears through the air (air conduction), we actually hear a great deal through vibrations in the bone (bone conduction). When a person with normal hearing hears their own voice, most of what they actually hear comes through bone conduction.
Problems in your outer or middle ear can block or restrict the flow of sound waves, preventing them from getting through effectively to your inner ear. A hearing aid relies on forcing enough sound through these problem areas, whereas bone conduction implants uses the body’s natural ability to transfer sound. By exploiting the full potential of this natural process – you can hear better and clearer than ever before.

How it works
While a hearing aid tries to push sound through the damaged area, a Baha System uses the beauty of bone conduction to send clear, crisp sound directly to your inner ear. Today there are two types of Baha systems. Both offer unique Cochlear technology designed to help you hear and communicate with confidence.
- The sound processor captures sounds in the air.
- The sound processor turns the sound into vibrations and sends them through the abutment or magnetic connection to the small implant.
- The implant transmits the vibrations through the bone directly to your inner ear.
How bone conduction hearing systems work (Oticon Medical Ponto®)
Bone anchored hearing systems are designed to use your body’s natural ability to transfer sound through bone conduction. The sound processor converts sounds into vibrations which are then sent through your skull bone, directly to your inner ear.
A bone anchored hearing system consists of three parts:
- A small (3 or 4 mm) titanium implant that sits in the bone behind the ear
- An abutment that is seamlessly placed through the skin enabling the sound processor to be attached
- A sound processor that sits discreetly behind the ear
 |
 |
 |
The small titanium
|
The abutment without sound processor |
The sound processor on the abutment |
How bone conduction works
The sound processor clicks easily onto the abutment. Once attached, it picks up sound waves in much the same way as a conventional hearing aid. However, instead of sending these sound waves through the ear canal, it transforms them into sound vibrations, ready to send through your skull bone. Thanks to the direct connection between the sound processor and the bone through the implant and abutment, your skin does not dampen the sound vibrations, which gives a clearer sound.


|
|
When you click off the sound processor, for example when showering or sleeping, no sound vibrations are sent and your hearing will return to its original state.
The Ponto System is an example of Direct Sound Transmission. This provides the best amplification and output, as compared to skin drive systems, where the skin creates a dampening layer between the sound processor and the bone.
|
|
|
|
|
|



