THYROID DISEASES
What is a thyroid gland?
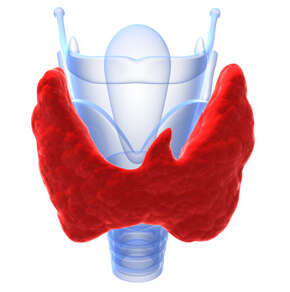
Thyroid gland is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the front part of the neck, under the throat. The thyroid gland is one of the hormone-releasing glands in the blood and has a very important role for our body. The thyroid glands release tyrosine (T4) and tyryodothyronine (T3), the so-called hormones. These hormones regulate the metabolism rate of your body and help control the energy levels of your body.
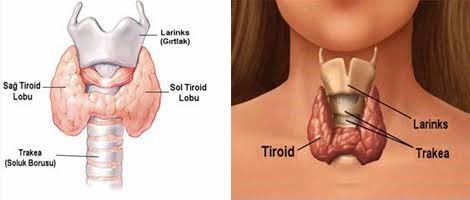
What is Thyroid Diseases
Since the thyroid gland is a hormone-releasing gland, the disorder in this function will cause various diseases. Hypothyroidism is called less hormone secretion, and hyperthyroidism is called much hormone secretion.
Hypothyroidism is the most common thyroid disease. It is more common in females and increases in the incidence with age. The most common cause of hypothyroidism is Hashimoto thyroiditis. In this disease your immune system attacks your thyroid gland and hinders it from producing enough hormone. Hypothyroidism can also be seen from birth due mainly to the treatment of radioactive iodine used in the treatment of other thyroid diseases, as a result of surgery and also due to the non-development of the thyroid gland.
The most common cause of hyperthyroidism is Graves’ disease. The thyroid gland grows and begins to produce excessive hormones. This disease is hereditary and depends on the immune system. Antibodies to the thyroid gland in the immune system stimulate the thyroid gland to produce more hormones than normal. Other causes include excessive thyroid hormone intake and thyroiditis (thyroiditis). The overgrowth of the thyroid gland (goitre) and the formation of nodules in the thyroid gland are also unusual.
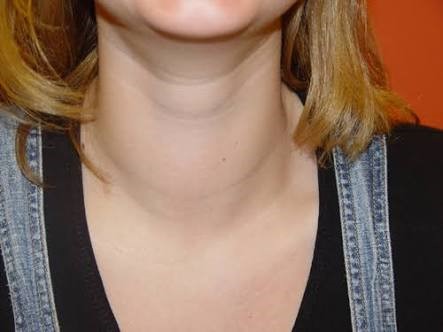
Goitre
What are the symptoms of thyroid diseases?
People with hypothyroidism may experience fatigue, fatigue, lack of attention, lack of resistance to cold, thickening of the skin, loss of hair and eyebrows, stabbing, bradycardia (slowing of the speed of the swallowing), hypertension, constipation, facial edema and menstrual disorders. In people with hyperthyroidism, people with hyperthyroidism may have problems with excessive nervousness, sleep disturbance, restlessness, lack of attention, emotional imbalance, aggressive attitude, trembling hands and feet, warmth intolerance, weight loss, tachycardia (increased heart rate), shortness of breath, Eyeballs (exoftalmus), musculoskeletal system disorders can be seen. Hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can be accompanied by thyroid gland growth (thyroid) and thyroid nodules, and they can manifest themselves with swelling in the neck. Thyroid gland normal functioning, however, there may be nodules in the thyroid gland and swelling in the thyroid gland may be seen.
What Should we done when thought of Thyroid Disease?
Thyroid gland diseases need to be very careful. There are various thyroid diseases, from simple goitre to cancer. Those who have mentioned the above should first consult a specialist physician. The surgeon then requests blood tests and thyroid ultrasonography in case of suspicion, following neck and other system examinations. These analyzes and examinations will make a diagnosis of the disease. These methods may require additional imaging methods and biopsy from the thyroid gland, which can not be diagnosed.
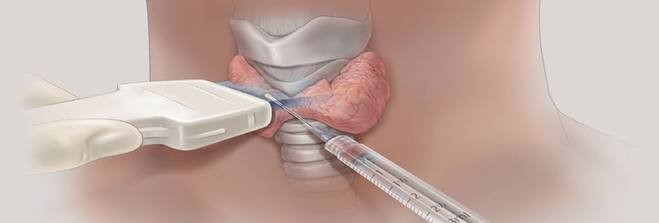
Ultrasound guided fine needle aspiration biopsy.
What to do in Treatment?
Thyroid hormone substitution therapy will be given for the deficiency in patients whose hypothyroidism has been found. Hyperthyroidism has no other treatment and usually requires lifelong medication
In patients with hyperthyroidism drugs are given to suppress excessive hormone production. If there is no decrease in hormone production despite these drugs, radioactive iodine can be administered. If no response is obtained despite all these treatments, finally thyroid gland is removed by surgical treatment.
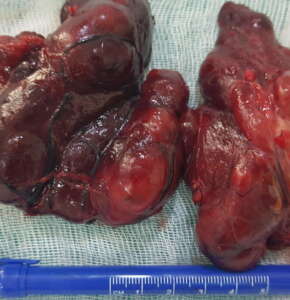
Thyroid gland can be surgically removed for aesthetic purposes and for relief of breathing if the thyroid grows too much or presses on the pitched tubule in cases where simple goiter is detected, ie only thyroid gland growth and no additional thyroid disorder.
If the nodules are over a certain size, biopsy is necessary. The biopsy result will be applied to the illness surgery which is reported as malignant or suspicious. If the biopsy result is benign, the patients are called at regular intervals and the nodules are followed up with ultrasound.
incision for thyroid gland surgery
Recommendations
The daily intake of iodine should be sufficient to protect against thyroid disorders. Especially in seafood, it contains enough iodine. In our day, iodine is put into table salt which we use daily. Non-thyroid disorders increase, so it is recommended to quit smoking. Those with thyroid disease in their family should consult a specialist in any indication who should be more careful.